EMI Calculator
An Equated Monthly Installment (EMI) is a fixed monthly payment made by a borrower to a lender on a set schedule, covering both principal and interest. It ensures full repayment of the loan over a specified period, commonly used for auto loans, real estate loans, and student loans. The EMI amount typically remains constant throughout the loan term, aiding in financial planning. Initially, more of the EMI goes towards interest, gradually shifting to principal repayment. Some banks offer reducing-balance EMIs where payments decrease with each installment.
How to calculate EMI?
EMI is a monthly payment that combines both the principal and interest to repay a loan over a specified period.
The basic formula that works in calculating EMI is as follows:
E = P x R x (1+r)^n/((1+r)^N – 1, where
E = Equated Monthly Instalment
‘P’ stands for principal amount
‘R’ denotes the applicable rate of interest
‘N’ stands for the loan term or tenure
Example of EMI Calculation
Imagine you’ve taken out a loan of Rs 10 lakh to construct a house. The lending institution has provided this loan at an annual interest rate of 7.2%, with a repayment period of 10 years.
As per the formula, the monthly loan repayment amount will be:
P x R x (1+R)^N / [(1+R)^N-1] where,
N is 10 years or 120 months
R is 7.2% = 7.2/12/100 = 0.006
EMI = Rs 10,00,000 * 0.006 * (1 + 0.006)120 / ((1 + 0.006)120 – 1) = Rs 11,714.
Hence, you will be paying the EMI of Rs 11,714 every month for 10 years.

What are the 6 Factors Affecting EMI?
Calculating EMI involves the loan amount, interest rate, and tenure. Adjusting these factors can increase or decrease the EMI:
1. Principal
The borrowed amount determines EMI size—higher loans mean higher EMIs; lower loans mean lower EMIs.
2. Interest Rate
Crucial for EMI calculation; lower rates mean lower EMIs, and vice versa.
3. Tenure
Longer terms reduce EMI amounts.
4. Down Payment
Higher initial payments can reduce EMI amounts.
5) Economic Factors
High inflation raises interest rates, increasing EMIs.
6. Pre-Payment and Foreclosure
Options to reduce remaining EMIs by paying off loans early.
Top 4 Benefits of EMI
1) Budget Friendly Approach
With EMI, people can afford their dream homes and vehicles through manageable monthly installments, making these significant purchases budget-friendly without the need for a large lump-sum payment upfront.
2) Increased Affordability
Various companies offer attractive EMI options, including zero-interest rates, which appeal to people and make purchases affordable through manageable monthly payments.
3) Creditworthiness
Timely payments improve a person’s creditworthiness and can lead to access to additional financial facilities.
4) Financial Discipline
Regular payments directly enhance financial discipline and contribute to increasing one’s credit score.
What are the top 4 disadvantages of EMI?
1) Longer Debts
Buying a house or car often means committing to monthly payments for 20 to 30 years, impacting a large part of your life with debt repayment.
2) Interest Charges Accrued
EMI is a convenient method for repaying loans, but the interest rate linked to the loan often results in paying more interest than the actual loan amount over time.
3) Skipping EMI Charges
If an individual misses their EMI, they will incur late fees, which add to the total amount owed.
4) Financial goals
Taking out a loan involves acquiring debt, and consistently paying it at a high interest rate each month over an extended period can affect one’s financial goals.
Types of EMIs Loan
1. Personal Loan
Fixed interest rate, used for vacations, medical expenses, and short-term needs. No collateral is required but higher interest rates apply.
2. Home Loan
Low interest rates, and long repayment periods (20-30 years). Home loan calculators estimate monthly payments and total interest costs. You can calculate through a home loan calculator.
3. Car or Bike Loan
Used for vehicle purchases. EMI is calculated based on vehicle cost, down payment, and loan tenure. Bike loan calculators help with calculations. You can calculate through a bike calculator and a car calculator.
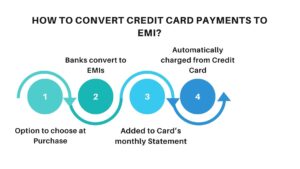
How to Convert Credit Card Payments to EMI?

1) Option to choose at Purchase
If you have funds available at the time of purchase, you can opt to make a down payment, with the balance amount being payable in easy EMIs.
2) Banks convert to EMIs
The bank structures the transaction amount into equated monthly installments (EMIs) according to the selected repayment period.
3) Added to the Card’s Monthly Statement
The EMI amount is included in the cardholder’s monthly statement.
4) Automatically charged from Credit Card
The EMI amount is automatically charged to the cardholder’s credit card each month until the entire converted amount is repaid, appearing on the monthly statement.
Key Factors to Consider When Converting Credit Card Bills into EMIs
1) Interest Rate
Banks charge interest on credit card amounts converted into EMIs. Timely EMI payments are essential to avoid additional interest charges.
2) Processing Fee
Converting credit card transactions into EMI involves processing fees that vary between banks.
3) Prepayment Options
Credit cards offer prepayment options for EMIs, allowing you to reduce the interest rate.
4) Reducing Balance Method
Interest is charged on the remaining loan balance each month. For example, if you pay Rs. 10,000 off a Rs. 40,000 loan, next month’s interest is on Rs. 30,000, reducing monthly interest.
5) Penalties on Missed EMIs
If you miss an EMI due date, penalties apply. To avoid this, enable auto-pay for timely payments.