Uses of Credit Card
1) Easy access to credit:
A credit card is convenient to use, allowing you to access funds immediately and repay them later. It can be linked to your bank account and digital wallet for easy access to money. You can simply scan and pay or swipe your card at a merchant’s terminal.
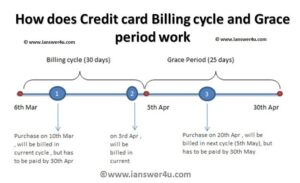
2) Interest free credit:
Users can access funds through a credit card without incurring interest charges. A credit card typically has a 45-day billing cycle, including a grace period, allowing you to use the money interest-free during this time.
3) EMI Facility:
If you want to pay for a new phone, house, or anything else, you don’t need to pay a lump sum or take out a loan. Instead, you can use a credit card and pay in EMIs (Equated Monthly Installments).
4) Reward points:
By using your credit card for expenses, you can earn reward points that can be redeemed for shopping, movies, and other benefits.
5) Improves your credit score:
If you know how to use a credit card wisely, you can improve your credit score and qualify for loans with minimal interest rates. Using a credit card and repaying on time boosts your credit score.
6) Keep track of your expenses:
Since credit facilities can lead to increased spending, it is important to track your expenses. With a credit card, you receive a monthly statement, allowing you to decide on a repayment date and effectively manage your credit.